Alexander A.Shpilman (alexandrshpilman78@gmail.com )
The physical
properties of "axion (spin) fields"
Let's try to present an expanded version of the article N1/98.
If we could have a
microscope that allows us to see objects smaller than 10-15 meters, we could
probably see interlacing of spiral structures (filaments and films) in the
place of electrons and protons.
At the same time, the
electrons and protons are composed of spiral structures, and it is probably
difficult to separate the interlacing of spiral structures, which refers to the
electron, and that to the proton.
Most likely, the spiral
structures in the atom are immobile. And their multiple twist (spiral into a
spiral) creates the whole set of quantum mechanical values of the states of the
atom.
1. There is a flow of energy (mass) of high density along the NEEDLE of the spirals. It has a pseudo-charge creating a magnetic field. Perhaps this is a longitudinal-transverse unipolar electromagnetic wave.
2. The
STREETS have a very large energy density and a large non-linearity of the
vacuum. This nonlinear nature violates the principle of superposition of
electromagnetic fields - the "electric charge" begins to interact
with the electromagnetic field. The properties of the vacuum vary greatly along
the thread of the spiral (The electromagnetic wave resistance of the vacuum for
an electron increases by a factor of 137/2.) N3/96).
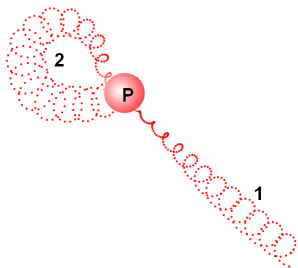
3. It seems that the
electron consists of two threads, twisted in a spiral, converging at one point
(the center of the electron), and having left and right polarization.
4. It seems that the proton consists
of three spirals (strands) with different combinations of polarization. In the
case of a proton: positive electrical pseudo-charges form two spirals, and
negative electrical pseudo-charges form the third (Fig.2, blue spiral 3). It is
possible, here is analogy of the thread-quark. All three spirals twist of one
"Moustache".
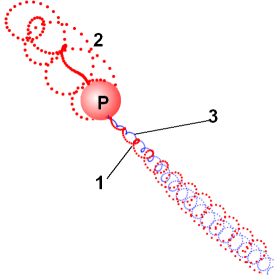
a)
But, in fact, there is actually only one spiral 1 (Fig.1) of positive electric
pseudo-charges (one quark is a positive charge and one quark is a negative
electric charge). Positive pseudo-charges, moving to the proton, do not
immediately fall into the center of the proton. They form a loop 2, skipping the center of the proton.
Or it is possible is version of the "inverted stocking" 2 in Fig.2. Probably this loop is the
second quark with a positive charge.
|
|
|
5. The
speed of energy movement is close to the speed of light along the string (in
our "gap" of time).
|
|
|
Fig.4 |
|
|
6. For a proton, for a
positively charged spiral 1, the
energy movement is directed from the periphery to the center of the proton. For
a negatively charged 3 the energy is
directed from the center to the periphery. But they rotate in one direction
moving in a spiral, forming spirals with left and right polarization.
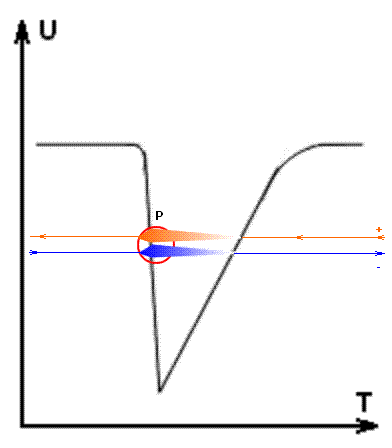
a/) Positive pseudo-charges
appear from nowhere (see Fig.3). They move to the center of the proton (P), increase their mass and disappear
in the center of the proton to nowhere. ..... Negative pseudo-charges appear
from nowhere in the center of the proton. They move from the center of the
proton to the outside, reducing its mass and disappearing into nowhere. It can
be assumed that positive pseudo-charges move from the future into the past (the
orange line), gradually manifesting itself in our time gap - "now",
and disappearing on the trailing front of the "wave of time". And
negative pseudo-charges move from the past to the future (the blue line),
manifesting itself in our gap "now" and gradually disappearing on the
leading front of the "wave of time", leaving for the future (see Time - Overtime).
b/) It is possible,
basically the spiral structure is stretched along the time coordinate T in the space (4,1) - see Time - Overtime. And in our "gap" of
time, this spiral is manifested in the form of a torus (ring) of large
concentration of energy. If we proceed model I.M.Matora, (I.M.Matora, "Model
of the structure of an electron and a muon," Joint Institute for Nuclear
Research, Dubna, February 4, 1981, calculations were
performed for a ring structure.) for an electron, the diameter of the ring
thread Is 1.4 * 10-106 meters, the magnetic field strength is ~ 10100Gs,
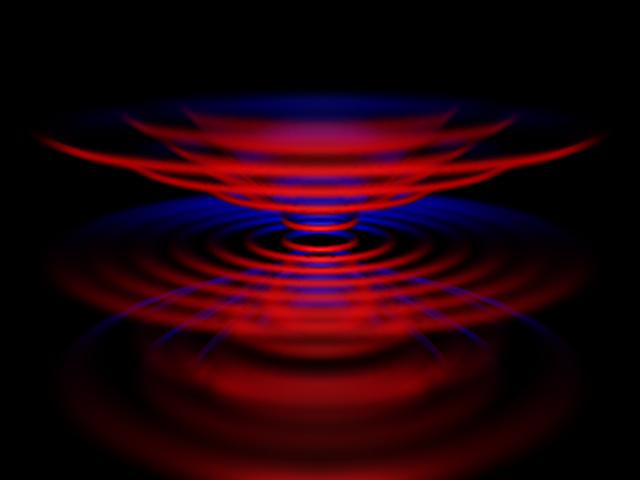
the diameter of the revolution is equal to 3.9*10-13 meters. It is
probable interference rings are formed around the main ring (interference
"reflections" of the main ring), similar to that shown in Fig.4.
c/) The spiral structure can
appear in our "gap" of time: during the motion of a proton
(electron); in potential fields and their gradients; and in the state of
spectral deformation - DS-state elements (see Time
- Overtime). Interferential spiral structures (interference
"reflections" of the main spiral structure) are formed around the
main spiral structure.
7. The
speed of spread a dither along the spiral (in our "gap" of time) is
much less than the speed of light and it is determined by the longitudinal
moment of the pulse and by the parameters of the environment (the density of
the spiral coiling changes).
8. The
material manifestation of these spirals is the so-called "axion
field".
9. An "axion
field" with unidirectional motion only positive pseudo-charges is called
an "axion field" of type 1
(see "Ring
structures "axion of fields""). The "axion field"
of type 1 is oriented in the
direction of negative charges to meet the vector potential and vector of the Poiting
10. An "axion field" with unidirectional motion only negative
pseudo-charges will be called an "axion field" of type 2. An "axion field" of type 2 is oriented in the direction of
positive charges to meet the vector potential and in the direction vector of
the Poiting.
11. An "axion field" of
counter motion opposite pseudo-charges will be called an "axion
field" of type 3. An
"axion field" of type 3 is
oriented in the direction of negative charges to meet the vector potential and
the vector of the Poiting.
12. An "axion
field" with a unidirectional motion of dissimilar pseudo-charges is called
an "axion field" of type 4.
An "axion field" of type 4
is oriented to meeting vector of the Poiting (if the
source of the field is considered to be a proton).
13. Interference copies of lower density are formed around the main spirals
of motion of pseudo-charges. They are especially strong for a "field"
of type 4. Interference ring strata
(rings ... -2, -2,1,2 ... ) are formed by closing the "axion field" of
type 4 in the ring. (Ring 0 in Fig.5) A chain of interference
ring strata is called an "axion field" of
type 5.
It is probable, it is possible to propagate the field
perturbation with a velocity exceeding the speed of light along the "axion
field" of type 5 (the
propagation of perturbations along the phase surface of the wave function).
Fig. 4 has executed Motorin
Oleg
Translation of
Irina Lis