Fig.1
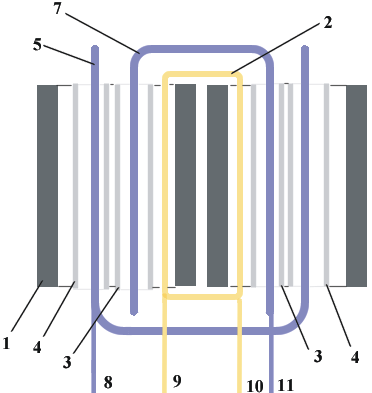
Fig.2
A.A.Shpilman (
alexandrshpilman78@gmail.com)The Optical Generator of Axion (Spin) Field
|
|
|
|
Practically in all generators of "axion field" there is a problem of retention of "axion field" in an active zone. Some generators were already described which use for retention of a field toroidal coils (see. N1/98, N2/98). Results of experiments on separation a component of "axion field" (see. N1/99) can be applied for effective retention of "axion field" in an active zone of generators. For an example we shall consider inproved construction of the optical generator of "axion field".
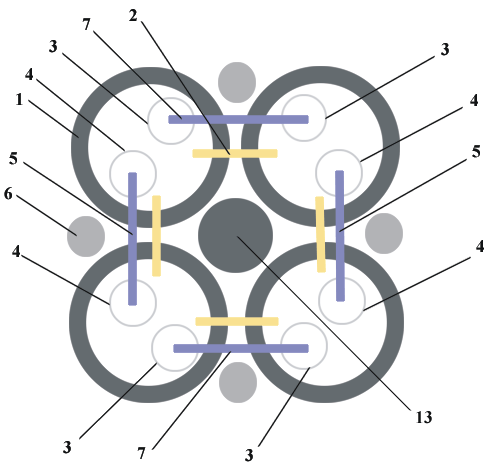
On Fig.1 side view of the generator is shown, and on Fig.2 the generatorís profile is shown. The generator consists of four ferrite tubes 1, on which wind the electrical coils 2. On coils 2 the electric current moves in such a manner that vectorial potential in the next ferrite tubes 1 is opposite directed. Into ferrite tubes are inserted two aluminium tubes 3 and 4 (from a foil). Through tubes 3 is passed lightguide 7, and through tubes 4 is passed lightguide 5 (naturally, it is desirable to fill by lightguide whole volume of ferrite tubes).
If on a contact 9 of coils 2 to feed plus, on a contact 10 minus of voltage, and ends 8 and 11 of lightguide 5 and 7 to connect to a high-power (pulse) light source, that in aluminium tubes 3 it will be necessary to feed positive voltage and in tubes 4 - negative.
During activity of the generator, the "axion field" having negative electrical pseudo-charge, will be deflect inside of a tube 3 into lightguide 7 with a counter direction of a flow of light and vectorial potential, so the "axion field" will be directional along a flow of light (from the end 11). The "axion field" having positive electrical pseudo-charge, will be deflect inside of a tube 4 into lightguide 5 with an agree direction of a flow of light and vectorial potential, so the axion field will be directional to meet a flow of light (to the end 8 in both cases counter-clockwise on Fig.2).
|
|
By activity of the generator two beams of "axion field" are formed going away upwards and downwards along an axis of the generator (length is determined by density of a light flow and size of vectorial potential), and also toroid is formed, (external) round the generator (ferrite tubes) with precise borders. Perimeter external "axion field" of toroid decreases up to perimeter of the generator with the assistance of cylinders 6 of an "Rose's metal" (Alloy: Bi - 50%, Pb - 25%, Sn - 25%) or tin, in which there is counter "short circuit" of "axion fields" to an opposite electrical pseudo-charge. Length of axial beams also limits by counter "short circuit" of "axion fields", with an opposite electrical pseudo-charge, in air on some distance from the generator. Due to this "axion fields" presses (because of the internal reasons), density of "axion field" inside the generator and in a beam is increased.
For obtaining the generator with unidirectional radiation, the lower beam can be blocked ("to close") by thin plate copper 12 (see Fig.3) tinned from all sides by "Rose's metal" (or tin).
The effectiveness of the generatorís work is higher than the optical generator described in N2/98 because the longitudinal moment of pulse of both component of "axion field" increases in it by light flow.
***
If to a design of the generator to add a ferrite core 13 (see Fig.1), a beam of "axion field" becomes tight and more dense.
About the further improvement of the generator read in N4/99.
(see N3/95 , N5/95 , N2/96 , N3/96 , N2/97 , N1/98 , N2/98 , N1/99)