Alexandr A.Shpilman ( alexandrshpilman78@gmail.com )
Observation of an "Axion (Spin) Field"
(project)
It
is not possible to touch and to see electrical and magnetic fields. But here is
the "axion field" which is possible both to
touch and to see. Those who have the COMFORT
generator can convince themselves in it.
In
order "to touch" the beam of the generator, it is not necessary to
place a hand directly in this beam. It is necessary to bring a hand slowly to
the beam sideways and to listen to the sensations. If you put your hand too
close the beam will pass through it and you will not have any
"tactile" sensations. And, moreover, if you keep your hand in the
zone of the beam of the generator too long time you can be losses of sensitivity in your hand for some time. For the
generators " The Generator of the "Axion
Field " Sort 5"
and the generator described in " Feedback in Generators and Detectors
Axion (spin) Field" this time can make some seconds.
The
beam of the generator can be seen if you look similarly like we do when we
notice an air haze above a heated object. For this purpose it is necessary to
focus the sight on the point located a little bit further the observable beam
of the "axion field". Moving the point of
our sight’s focus deeper, we can make out various structures of the beam of the
generator.
If
our usual sight is capable to see the beam of the "axion
field", there is a desire to photograph this beam. But, alas, even to
photograph air mirage above a heated object is not simple. It is even more
difficult to photograph a beam "axion
field".
In
our case the habitual for physicists method of
photography of optical inhomogeneities in
interferometers is not useful. First, the beam of the "axion
field" refracts light not unsystematically but casually. Second,
apparently, light refracts resonantly. As we do not know resonant lengths of
light’s waves it is better to use white light instead of monochrome light of a
laser in an interferometer.
|
|
|
|
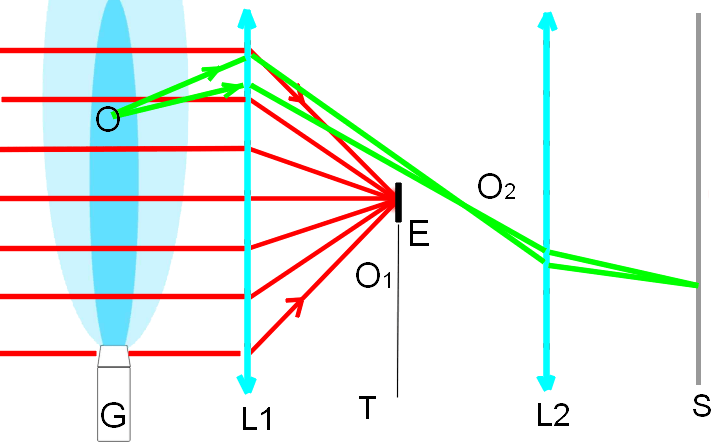
It
is possible to use a shadow method for photography of the beam of the "axion field" of the generator G (see Fig.1). In this method the parallel
stream of light transparents the beam of the "axion field", and it is focalized by the lens L1
(see Fig.1) in a point of focus O1. The small, absorbing barrier E
is placed in the point of the focus O1. This barrier is completely overlaps a stain of
light in this focus. Light scattered by the beam of the "axion field" in the point O is focalized by the
lens L1 in the point O2 outside of the absorbing barrier E
and then is focused on the screen/photographic plate S by the lens L2.
Thus, on the screen/photographic plate S we shall see only light scattered
by the beam of the "axion field". We shall
have a photo of the beam of the "axion
field".
A shadow method
is good only in laboratory requirements. It is more interesting to try to use a
method of an optical tomography, which doesn’t need a parallel stream of light.
In usual object-glass cameras the purpose of achievement of the maximum depth
of sharpness is pursued. The opposite purpose is in an optical tomography – it
is necessary to achieve the minimal depth of sharpness of a lamina of a viewed
object and to cut off light, which radiates from objects outside of this
lamina. This problem is solved successfully by a human eye observing the beam
of the "axion field". And this problem is
not capable to solve by a usual camera.
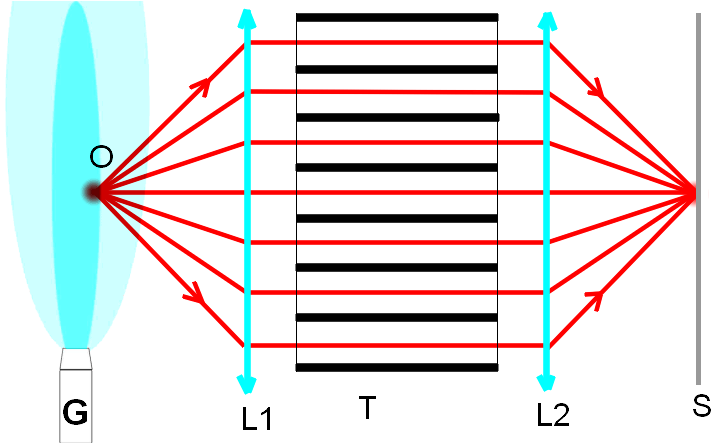
For
an optical tomography it is possible to use the design, which is shown in
Fig.2. Light scattered by the beam of "the axion
field" of the generator G in the point O is transmuted into
a parallel stream of light by the lens L1. Then the parallel stream of light transits through a set of blacken, long and
thin tubes T. Light is focused in the screen/photographic plate S
by the lens L2. Light scattered in points nearer or further than the
point O will not form a parallel stream of light after the lens L1.
It will be absorbed by the blacken walls of the tubes of the set T.
Thus, we can make out the thin structure of the beam of "the axion field" layerwise,
changing a focal distance of the lens L1.
Instead
of the set of the tubes T it is possible to use special glass (the fibre optic plates), which is quasi welded from set of
glass optical fibrils with a blacken surface. Such glass is transparent if our
sight is perpendicular to the surfaces of the glass and it is opaque or black
from another angle of view. This glass is usually used in devices of night
vision and in some spectrometers.
Instead
of the set of the tubes and a special glass it is possible to use a set of
several stratums of a grid with the combined meshes. Instead of a grid it is
possible to use a color separation mask from a color television tube.
Certainly,
the description of the methods is simplified. It is necessary to have some
experience of operation with optical instruments for embodying the described
constructions.