Alexander A.Shpilman (alexandrshpilman78@gmail.com)
What is it "a dualism"?
Photon or the quantum light was the
course of rough debates in physicist community in due time. Two submissions
about a photon became a stumbling block:
1.The photon is a particle (a
corpuscle).
2.The photon is a wave.
Eventually it was accepted the Solomon's
solution: a photon is a particle with wave’s properties.
Recently physics incline to the
submission of a photon as a compact package (a team) of electromagnetic
radiation (EMR). But the reasons of stable existence of an EMR package are not
clear till this moment. It is not clear, if the photon has a wavelength (l=6*10-7
m - red light) in one thousand times exceeding the sizes of atom (d=5*10-11
m - hydrogen atom), how it manages to be radiated and to be absorbed by atoms
as whole and indivisible.
However we will try to receive a stable EMR
package. Let's assume that the following Maxwell’s set of equations for an
electromagnetic field is rather correct.
|
|
rot(E)=-d(m*H)/dt |
(1.2.1) |
|
|
rot(H)= d(e*E)/dt |
(1.2.2) |
|
Where |
E - electric field strength, |
If charges are deficiency
|
|
div(m*H)=0 |
(1.2.3) |
|
|
div(e*E)=0 |
(1.2.4) |
We can see from equations (1.2.3),
(1.2.4) follows, that the nondeliquescent EMR package cannot be received, but,
assuming, that, for example, dielectric permeability of vacuum e is not
the constant, and it is not a function from an electric field strength E,
then the situation already exchange.
If e is nonlinear, that what
values of E can we this nonlinearly detect? For this purpose
we shall define, what a photon strength EMR with a wavelength l=6*10-7
m. A photon energy is equal:
|
|
W=h*c/l |
(1.2.5) |
|
|
Where |
h – is a Planck's constant, |
||
Assume, that a photon basic energy
is concentrated in cube l*l*l, then from equation:
|
|
l2*(e*E2+m*H2)/2 =h*c/l, |
(1.2.6) |
assuming, that
|
|
e*E2=m*H2, |
(1.2.7) |
We will receive
|
|
E =400000 v/m |
(1.2.8) |
Such strengths of electric field are
already used for a long time and it was not revealed any changes e. So the submission:
|
|
e = e0+A1*E2+A2*E4+A3*E6+… |
(1.2.9) |
|
Where |
e0 - dielectric permeability of vacuum by a
deficiency of fields. |
will not lead to anything
interesting, as then A1, A2, A3, … should be
very small sizes and furthermore with the help of one focusing lens it is
impassible to made from a wide ray of light the narrow one.
But, if you would use a system of
focusing and dispersing lenses for compression and stabilization of the sizes
of a beam light, then this purpose will be accessible; i.e. we shall assume,
that on the forward front of an electromagnetic wave, where:
|
|
dE2/dt > 0 |
(1.2.10) |
will be
|
|
e > e0, |
(1.2.11) |
on a back side of a front of wave,
where:
|
|
dE2/dt < 0 |
(1.2.12) |
will be
|
|
0 < e < e0 |
(1.2.13) |
For a photon with l=6*10-7
m, taking into account (1.2.8), we can find:
|
|
max|dE/dt|*E*c/l
=2*1020 V/m*s |
(1.2.14) |
It is a sizeable size. If we want to
reach such size of derivative with rather small frequency of oscillations of an
electromagnetic field (EMF) in 2GHz it is necessary to create EMF with strength
in 10+11 v/m.
But such EMF strengths with such frequencies are unattainable yet and to measure prospective non-linearity e point-blank it fails. But, nevertheless, suppose, that:
|
|
e =F(dW/dt) |
(1.2.15) |
|
Where |
F - while unknown for us function |
Or it is more concretely (but with
the greater probability of an error in further constructions):
|
|
e = e0/(1-a* dW/dt)2 |
(1.2.16) |
|
|
There is can be an objection here:
with such version e the electromagnetic wave
will be not invariant concerning different frame of reference. But it is
possible to answer it such a way: there is own e in each system, and it
is more correct - e of the measuring instrument (material mass) in each
system, i.e. measuring instruments are not invariant and their indications
depend on those conditions, which they are in. For example, the clock goes
slower on a surface of the Earth then clock which is on moon.
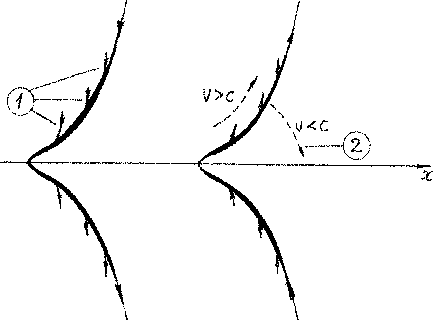
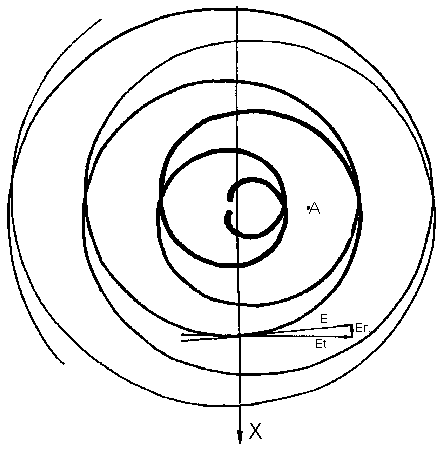
Now we shall try, based on the formula (1.2.16), to present a photon structure of (see Fig. 1, where: 1 - direction of an electrical field, 2 - direction of energy extent of an electromagnetic field.). We have on the forward front electromagnetic (EM) photon wave
|
dW/dt > 0 |
and
|
e > e0 |
e is the
more, than the speed of increase of energy concentration is more. Thus the speed of motion EM energy (V) less then
speed of light (c) and it has some component toward the direction of
center (the focussing is happening).
We have on the opposite side of EM
wave’s front of a photon
|
|
dW/dt < 0 |
and
|
|
0 < e < e0 |
Let's look
at Fig.1. It reminds the funnel or curved scissors. There is necessary to
recollect a mental experiment concerning speed determination of a cross point
of two edges of scissors (see Fig.2).
e is the
less then there was a concentration of energy more. In this connection
the speed of motion EM energy (V) is more then speed of light (c) and it
has some component toward the direction to the center (the defocusing is
happening).
Let's look
at Fig. 1. It reminds the funnel or curved scissors. There is necessary to
recollect a mental experiment concerning speed determination of a cross point
of two edges of scissors (see Fig. 2).
|
|
This speed is equal
|
|
U=V/Sin(a/2) |
(1.2.17) |
|
|
Where |
U - speed of motion of an edges’ cross point
to the direction X (phase speed), |
||
It is
visible from the formula (1.2.17) that the speed U can be arbitrarily
large. And it is clear: the cross point of edges is not a material skew field. Similarly it is possible to approach to our
"funnel" (see Fig.2), i.e., we can, selecting the various forms of
submission of relation (1.2.15), to receive any speeds of a photon motion as a
indivisible one with minor speed deviation of separate parts EM wave from
established speed of light. But it is necessary for stability of a photon in
order to the speed of a photon, as a whole, was less then a EM speed of energy
on back front its EM wave.
From our
"funnel-shaped" model of a photon follows, that the front EM wave of
a photon on a rim considerably advances its central part, where the main share
of EM energy is concentrated. Such a way, area of main concentration of energy
and even all photon can receive the information about obstacles, which are
located far from it, and can change a direction of their motion pursuant to
character of interaction. And, the last one will be already exhibited in
interaction of a photon, as a whole, with an obstacle.
The
interaction between photons is possible due to e nonlinearity. For
example, the ray of light from a far star consisting of photons with an
identical wavelength in an outcome of resonant interaction will become
coherent. The photons will align phases EM waves during traveling from a star
to the Earth (their motion will be possible to assimilate to motion of
coordinated ranks of the soldiers).
This
photon "funnel-shaped" model more approaches for two-dimensional
case. In our three-dimensional world the structure of
a photon will be a little bit more difficult. We can try to present how it will
look like rolling up the Fig.1 into a tube lengthwise an axis X. At that
case the ends of our "funnel" will be
crossed and we shall have one more "funnel". If we prolonging the
ends of new "funnel" we shall receive new crossing and new
"funnel" and so on. In the given model we
have not a "funnel" as such. There is a concentration of energy along
" bunches", curled (around a tube) in the right and the left-hand
spiral. EM energy of a wave goes along bunches, decelerating sequentially its
run and being concentrated in interception units (in this moment the photon is similar
to corpuscle). And then, departing along bunches, accelerates its run (in this
place the photon is similar to a wave), so that on the average speed of motion
remains constant.
We can
make a conclusion from the formula (1.2.17) that the more e is different
from e0, the more is a photon energy (E is more and
its speed of change is more - frequency f), so the more possible is
interaction between photons.
At
interaction of two gamma-quantums (photons with large energy), having EM
frequency of oscillations
|
|
f > m*c2/h =1.2*1020 Hz, |
(1.2.19) |
|
Where |
m - weight of an electron, |
Wavelength
|
|
l < c/f= 2.4*10-12 m |
(1.2.20) |
And strength of a field at the EM
wave front
|
|
E > ( h*c/(e* l3)0.5=2.5*1016 V/m, |
(1.2.21) |
As we know
from practice, the pair of particles can be born: an electron and a positron.
Let's try
to construct a model of an electron from EM waves.
If we try
to construct model of an electron now, studying the mechanism of interaction of
two gamma-quantums with formation an electron-positrone pair, then we would not
be able to make it. It will be not so simply to clear up in the mechanism of
formation an electron-positrone pair even somebody will be possible to
photograph this moment to the smallest details. Therefore
we shall try to approach to this problem from the other end.
At first we shall recollect, that we know about an electron.
The electron has:
1) Weight
m = 9*10-31 kg;
2) Charge q = -1.6*10-19 C;
3) Spin (something like a torque of an electron about the axis);
4) Magnetic moment.
As for
weight, there are not any problems: EMF has gravitational weight too. But here
the electron charge will be most difficult. But, nevertheless, we shall try to
investigate, that means next expression: the electron has a charge. It means,
that the electrical field round an electron is directed from different
directions mainly to its center.
|
|
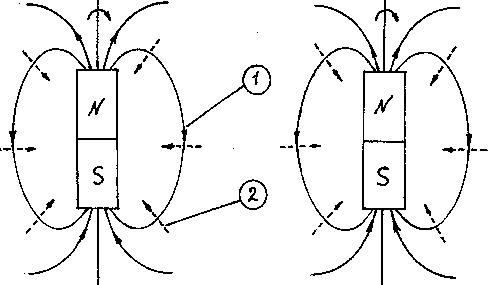
Let's try
to receive it. Let's take two cylindrical constant magnets and twirl them
counter-clockwise round the axes. Now we allow, those together with magnets
their magnetic fields will be twirled round their axes also. Then the traveling
magnetic field will call an appearance of an electrical field, which will be
mainly directed to center of magnets, i.e. we will receive some analog of an
electrical field of a charge (see 3, where: 1 - magnetic field, 2 - electrical
field).
Thus, one
after another of magnitude order the strength of a magnetic field will be was
equal
|
|
H ~ 1/R3 |
(1.3.1) |
Where R - distance to center
of a magnet,
Its moment
|
|
M ~ R |
(1.3.2) |
And electric field strength
|
|
E ~ M*H ~ 1/ R2 |
(1.3.3) |
It is necessary to mark, that the
observable electrical field of an electron is equal
|
|
E= q/e*R2 |
(1.3.4) |
|
|
The
amazing coincidence! But, as it is visible from Fig.4 (where 1 - vector of an
electrical field) the electric field strength is heterogeneous, i.e. there is a
large quadrupole moment. The maximum of electric field strength will be at
angles equal 45 and 135 degrees. And one larger defect is - the strength of a
magnetic field concerning its energy is comparable to energy of an electrical
field, and an electron has the energy of a magnetic field, which is
significantly less.
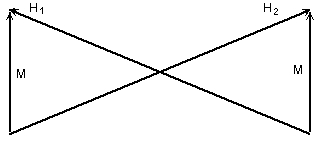
Let's try
to reduce strength of a magnetic field. For this purpose
we shall turn over the second magnet for 135 degrees and we shall mentally
superpose two magnets, rotated round the axes such a way their centers have
coincided. In this connection the magnetic field is
almost completely compensated, the electric field strength is doubled, and the
quadrupole moment decreases, i.e. the electrical field will become more
homogeneous. The residual magnetic moment is a magnetic moment of an electron
(see Fig. 5, where H1, H2 - magnetic moment
of constants magnets; M - resultant moment).
|
|
The model
is and reflects some electron properties, but, nevertheless, is rather rough.
Let's try to replace our two constants of a magnet with two spiral EM-waves
(see Fig.6). They move to center, are curled in the opposite parties (vector of
an electrical field direct along spirals to center). Thus, the rotation axes,
directional in space the same, as were directed magnets (under 135 degrees
between axes).
Now we
draw analogy with our model of a photon, i.e., on forward front EM of a wave
moving to center, we have e > e0 and speed U
< c, and on back front EM we have waves 0<e<e0
and speed U>c.
|
|
In this
connection EM energy moves to center on forward front EM wave, and EM energy
moves along a wave front from center on back front EM wave. Equality of these
flows of energy is a necessary condition for stable existence of our model.
And, if we reason correctly, this small island of stability corresponds to rest
energy of an electron.
Thus, we
have received electromagnetic -wave model of an electron. This model does not
require any attraction of a hypothetical rotated magnetic field and has a
number of interesting new properties.
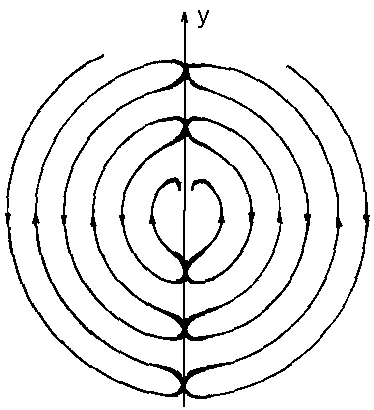
We imagine - ours EM model of an electron moves as whole along an axis X with speed
V. Then in a point "A" EM wave moved to the direction to an
axis X and it will increase the frequency of oscillations (according to a
special relativity theory):
|
|
w1=G* w0 |
(1.3.5) |
Where
|
G=1/(1-V2/c2)0.5 |
(1.3.6) |
And EM wave moving to the opposite
party, will reduce the frequency of oscillations:
|
|
w2= w0/G |
(1.3.7) |
In consequence, the straight line,
connecting points ("A") of interception two EM waves, will become
bent to the party of our model’s motion and we shall observe beatings of
strength EM field on this straight line with frequencies:
|
|
f1= w1+ w2 |
(1.3.8) |
and
|
|
f2=| w1- w2| |
(1.3.9) |
|
Where |
f1 - high-frequency component, |
Let's consider only low-frequency
component.
|
|
f2= w1- w2=
w0*(G-1/G)= G*w0*V2/c2, |
(1.3.10) |
With V is significant smaller
C, we have:
|
|
f2= w0* V2/c2=m*V2/h, |
(1.3.11) |
Where m - weight of an electron.
In the total
we have received de Brojlya formula for frequency, and from here we can find a
wavelength de Brojlya (wavelength of probability of electron detection in a
point "A"):
|
|
l=V/f2=h/(m*V) |
(1.3.12) |
The amazing coincidence! It is look like that we are going to the right direction. But we should be without any emotions. Let's look, whether all is so good, as it seems. It is visible from Fig.6, that only small part of an electric field strength has a direction to center (radial component - Er), the main part - is perpendicular to a direction to center (tangential component - Et). As it is visible from the formula
|
|
Er= l*Et/(2*Pi*R) |
(1.3.13) |
|
Where |
R - distance to a spiral center, |
Er - component decreases with a distance. If we
would ignore this moment, than for obtaining relation Er
from R, as with the electron (the formula 1.3.4), it is necessary
|
|
Et=K/R |
(1.3.14) |
Where K - proportionality factor.
It will mean, that the electron will
have indefinitely large energy of rest and, as a result, - indefinitely large
weight. The given conclusion can be checked up, integrating EM density on all
volume taken, by model (from l to endlessly). The situation will not be
betterment so much, if our electron model present as a flat: the energy of rest
will be received indefinitely large all the same.
What is our error in?
It is
consisted in that we did not give our attention to interception’s points of
helical (exacter-spiral) EM waves, and the interaction between EM waves will
happen here and the wavefront should be deformed, how is shown in Fig.7. If
this picture is right, that, obviously, that basic EM energy of our model will
be concentrated in interception’s EM units of waves and the vector of an
electrical field of units will be mainly directed to center of model. Thus, Et
will not already play the special role and, on the supposition of that Er
decreases in units with the same distance as and in the formula (1.3.4), rest
energy of our model will be quite certain (final) size.
|
|
It seems
it is not quite all right in our new model again. The basic energy was
concentrated along one axis (axis Y on Fig.7). Let's name this directivity
"a charge vector" (CV), which is creating, on the first sight,
enormous quadrupole moment, which would be detected a long time ago. But there
is one "but" here. When we construct model of electron we accepted,
that there is the speed of EM energy propagation exceeds speed of light on
return front EM waves, and it means, that the unit of interception spiral EM
waves can move along their front with speed, greater then speed of light. Thus,
the availability at an electron CV will be exhibited absolutely differently, than quadrupole moment at a usual dipole.
This model
of an electron has area of the greatest concentration of energy in the shape of
the disk, is considerably extended along an axis Y and is bent along it in a
direction of an axis Z.
The
concentration EM energy along one axis Y happens in rare cases, when energy of
both helical waves is identical. Usually their energies are not equal. Their
wavelength is not equal either, that results to motion of EM waves units of
interception on a spiral round an axis Y, in such a manner that, one
"MOUSTACHE" (for example: CV oriented along an axis Y) has an
exterior of a left-hand spiral, and other - right-hand. Thus, the electron has
a spin (S) and magnetic moment (M) (as a coil copper with direct current has).
As a rule,
spiral bunch of electron’s MOUSTACHE swirls in a spiral too (spiral of the
second order) under the influence of external forces. And, this second order
spiral can be left or right. It is possible to name motion of electron energy
along of the second order spiral as orbital motion with a moment L.
The
combination of spirals of MOUSTACHEs curling’s direction of the first and
second level is a combination of possible a spin S orientation and orbital
moment L.
If the
direction S and L coincides, it results that outside of spirals the strength MF
adds, and inside - is deducts. In an outcome inside of
external MF spiral becomes ring-shaped and less then external MF (because
fields S and L are intersected under an angle), that results to compression of
an external spiral’s diameter. This condition is characterized by a large
electron magnetic moment, causing to orientation of an electron’s MOUSTACHE
along external MF with strengthening of the last one.
If the
direction S and L is opposite, it result that outside
of spirals the MF strength deducts and inside - adds. As a result
MF becomes ring-shaped in an external spiral. In such condition
the electron is characterized by a small magnetic moment. At that, the
moustache of an electron has a tendency to twirl into a spiral of the third
level under the influence of external MF. External MF of a MOUSTACHE directed
against external MF, i.e. such electron exhibits its diamagnetic properties. If
on an electron's electrical field (EF) with opposite S and L to impose a proton
EF such a way that on a macroscale, on the average, EF was equal to zero, but
the availability of such CV will be rather difficult to detect. The last variety
CV field is, probably, so-called an "axion field" (AF). AF is
unstable and has a tendency to decay on particles, which are similar to a
neutrino with a rest mass that is not equal to zero. These particles are
characterized by four main qualities - weight density of energy, frequent
spectrum and topology. Let's name them "Quons"?.
A proton
model which we can construct by analogy with an electron model, adding to
already being available two EM waves a third one such a way, that the angle
between direction planes of propagation EM waves was in the order of 120
degrees. In an outcome of it the area of the greatest EM energy concentration will
consist of three MOUSTACHES.
Proton’s
MOUSTACHE intertwine along their axes the same way, as
an electron does. But, a proton has three MOUSTACHE
and it can result in torsion them among themselves into one MOUSTACHE (other
versions are possible). It'll have minimum magnetic moment (magnetic moment of
an electron Me=9.3*10-24 J/T, and magnetic moment of a proton
Mp=1.4*10-26 J/T, i.e. Mp < Me almost in a
thousand of time).
It is
natural to begin consideration of an atom structure with an atom of hydrogen,
consisting of one proton and one electron.
The
electron becomes inside of a conical MOUSTACHE of a proton at interaction of an
electron with a proton. That what one MOUSTACHE of an electron interact with a
MOUSTACHE of a proton becomes to be directed to the a
proton’s side, and, at that the second MOUSTACHE of an electron is pushed out
sideways, because the direction of EF is opposite to EF of a proton’s
MOUSTACHE.
In
consequence of such interaction there will be getting out two MOUSTACHES in
different directions beyond the bounds of our model of hydrogen atom. One
MOUSTACHE of an electron and second one - a MOUSTACHE of a proton with
compensated by halves EF.
Such atom
will have a large electrical dipole moment and, as a result, a large
reactionary ability.
If two
hydrogen atoms interaction then their free MOUSTACHES are mutually closed such
a way, that outside of a arise hydrogen molecule
remains a very little and as a result the relatively inert gas is received.
This
molecule strongly reminds atom of helium. If we shall bring together protons
and we connect them into a nucleus by neutrons, that we shall receive atom of
inert gas helium.